Concerned about crypto taxes in South Africa? No need to worry! This guide provides clear and simple instructions for filing your Bybit taxes in South Africa. From understanding your tax responsibilities to completing your taxes with crypto tax software like Catax, we cover everything you need to know.
- Latest Crypto tax updates in South Africa
- What is the tax rate for trading crypto in South Africa?
- Can SARS trace Crypto Asset Transactions?
- Crypto Transactions that are Subject to Tax in South Africa
- Investor vs Trader
- How South Africa Taxes Crypto
- Is there any way to reduce my crypto taxes?
- What happens in South Africa if I fail to file my crypto taxes?
- Using Catax to Manage Your Bybit Taxes in South Africa: A Simplified Process
Do I need to pay tax on my cryptocurrency in South Africa?
In South Africa, taxes apply to earnings generated from activities involving cryptocurrencies such as trading, selling, or mining. When profits are realized from the sale of cryptocurrencies, Capital Gains Tax must be paid accordingly. Adhering to South African tax regulations mandates the inclusion of cryptocurrency earnings in your annual tax return.
So, if you’re trading on Bybit or any other platform, you’ll likely have to deal with “Bybit tax in South Africa”. And remember, Catax can help make figuring out your crypto taxes much simpler.

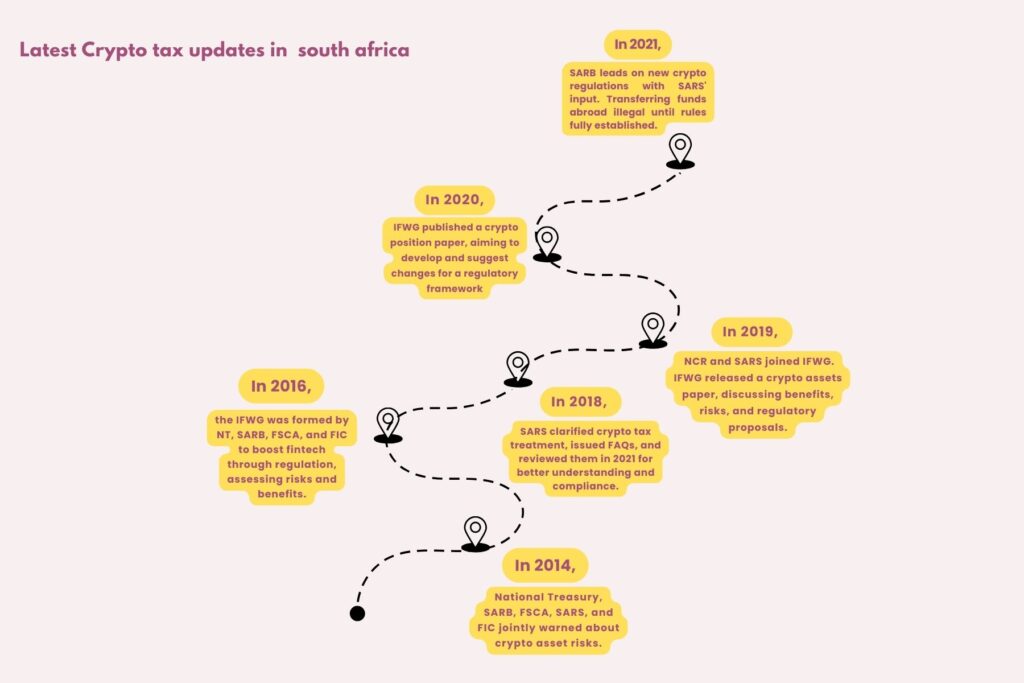
Latest Crypto tax updates in South Africa
In South Africa, crypto assets fall under the category of ‘assets of an intangible nature’ for tax purposes. SARS has intensified regulatory oversight to ensure tax compliance within the crypto industry. Additionally, individuals can benefit from an annual capital gains exclusion of R40,000, after which 40% of any remaining gain becomes taxable. Furthermore, SARS treats crypto transactions, including trades and payments for goods or services, as barter transactions and subjects them to capital gains tax at a rate of 18%. Also, SARS aims to combat tax evasion and promote transparency by adopting the OECD’s Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF). Furthermore, compliance and enforcement efforts are leveraging blockchain technology to track and audit crypto transactions, signaling a shift towards more sophisticated regulatory measures.
What is the tax rate for trading crypto in South Africa?
South Africa treats cryptocurrencies as intangible assets for tax reasons. Tax authorities are keeping a closer watch on crypto to make sure everyone pays what they owe. You don’t pay taxes on the first R40,000 of profit, and 40% of any profit above that is taxed. Trading crypto or using it to buy things counts as a swap deal, with taxes on the profit at 18%. SARS is adopting international rules to prevent tax dodging and to be clearer about crypto dealings. Also, they’re using the technology behind crypto to track and check its use, showing they’re getting smarter about regulation.

Can SARS trace Crypto Asset Transactions?
Yes, the South African Revenue Service (SARS) can trace crypto asset transactions. Also, the Income Tax Act gives SARS a lot of collection powers. One of these is the ability to force third-party service providers to send in financial information. SARS makes sure that crypto assets pay their taxes by using secret auditing and enforcement methods.
Moreover, SARS has aligned with the Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF), a global initiative developed by the OECD. This move signifies SARS’s commitment to enhancing tax transparency and combating tax evasion in the crypto sector. The CARF wants to make it easy for different places to automatically share information about crypto transactions with each other. Standard rules for reporting help make sure people pay the right taxes on their crypto activities. This is important because crypto deals often happen without much oversight. SARS is keeping up with the growth of cryptocurrency and setting rules to make sure taxes are fair and followed in the market.
Crypto Transactions that are Subject to Tax in South Africa
In South Africa, SARS treats cryptocurrency as intangible assets for taxation purposes. Individuals are entitled to a R40,000 tax exemption on capital gains. Beyond that threshold, a tax rate of up to 18% applies. Any activity involving selling, trading, or using crypto for goods is considered taxable. Also, Crypto transactions and purchases are treated akin to swaps, and any profits are subject to taxation as gains.
If you mine, stake, get airdrops, or hard fork income, it’s taxed up to 45% as income. But, holding it long-term might just tax you 18% as gains. Whether it’s taxed as gains or income depends on your intent and actions. They suggest using a FIFO method for accounting, but you can also pick another way. Therefore, it’s key to know these tax rules and maybe get a tax expert’s advice. At last, Crypto tax details can be complex and vary by your situation.
| Transaction Type | Capital Gains Tax (CGT) | Income Tax | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selling crypto for fiat | ✔ | ❌ | CGT applies if held as an investment, after R40,000 exclusion. |
| Swapping crypto for crypto | ✔ | ❌ | Treated like selling for fiat, may attract CGT. |
| Spending crypto on goods/services | ✔ | ❌ | Seen as barter, might be subject to CGT. |
| Gifting crypto | ✔ | ❌ | Subject to CGT, with specific exclusions. |
| Mining crypto | ❌ | ✔ | Counted as income and taxed when received. |
| Receiving crypto as payment | ❌ | ✔ | Taxed as income at market value when received. |
| Staking or lending rewards | ❌ | ✔ | Considered income, taxed upon receipt. |
| Airdrops | ❌ | ✔ (Assumed) | Likely treated as income, despite lack of clear SARS guidelines. |
| Buying and holding crypto | Not taxable until sold or otherwise disposed | ||
| Transferring crypto between wallets | Not a taxable event. |
Investor vs Trader
To file Bybit taxes in South Africa, the method by which the tax authorities assess your crypto trades depends on whether they categorize you as a crypto investor or trader.
- Investors: They receive a more lenient tax treatment. Upon selling crypto assets and realizing a profit, that profit becomes liable to Capital Gains Tax (CGT). The initial R40,000 of your annual gain is exempt from taxation. Subsequently, 40% of the remaining gain is subject to taxation at rates of up to 18%. Transactions like trading one cryptocurrency for another or utilizing crypto for purchases are categorized by tax authorities as ‘barter transactions,’ and the profits from these are taxed as capital gains.
- Traders: Traders, on the other hand, in South Africa face a heavier tax burden. If you engage in frequent cryptocurrency trading, your profits are subject to taxation as income at the marginal income tax rate, beginning with the first rand you earn. While you do not benefit from the R40,000 exemption, you are eligible to deduct expenses directly associated with your trading endeavours.
For example, if you hold an asset for more than three years, you usually consider it an investment for CGT purposes, highlighting your intent’s importance when you buy or sell.
Investment or trader taxation depends on your intentions and how often you purchase and sell crypto. Investors maintain assets for lengthy durations to increase capital. Traders buy and sell crypto regularly to profit from market swings. SARS considers crypto an intangible asset but hasn’t established crypto tax laws.
Remember, it’s wise to seek advice from a tax professional who understands both the crypto market and South African tax laws. Furthermore, this ensures you stay compliant and optimally manage your tax obligations.
How South Africa Taxes Crypto
To file Bybit taxes in South Africa, you must first understand how crypto assets are taxed. They are subject to normal income tax rules, and also taxpayers must declare their gains or losses as part of their taxable income. SARS has the authority to enforce tax obligations through various powers, including requiring third-party service providers to report financial data.SARS has adopted the Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF), a global initiative to enhance tax transparency and combat tax evasion in the crypto sector.
Is there any way to reduce my crypto taxes?
In South Africa, authorities view cryptocurrency as an intangible asset. Also, SARS watches crypto trades closely to regulate fintech. Individuals can make up to R40,000 in capital gains tax-free annually. But beyond that, they must pay an 18% tax on 40% of their remaining gains. To lower your crypto tax burden, consider these strategies:
- Harvesting losses: Selling assets at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce your tax liability.
- Receiving crypto as a gift: Not considered a taxable event. However, it’s important to keep records for future disposals.
- Investing in cryptocurrency via an IRA or 401-K: This allows for tax-efficient growth of investments.
- Hiring a specialized crypto CPA: They can help identify strategies to minimize your tax burden.
- Donating cryptocurrency: This can provide tax benefits as it is not considered a disposal event.
- Taking out a cryptocurrency loan: Avoids taxes on disposals by using crypto as collateral for fiat currency.
- Relocating: Moving to regions with more favorable tax rates, though this is more extreme.
- Keeping detailed records: Essential for accurately filing taxes and potentially reducing your tax bill.
- Using crypto tax software: Automates the process of generating comprehensive tax reports.
These tactics are for lawful tax avoidance, not tax evasion, a serious felony. Also, to negotiate South Africa’s complex crypto taxation landscape, comply with local tax rules, and consult a tax specialist.
What happens in South Africa if I fail to file my crypto taxes?
In South Africa, the repercussions of not filing crypto taxes can be severe, potentially leading to a maximum prison term of five years for tax evasion or fraud. Furthermore, the South African Revenue Service (SARS) has the authority to levy penalties of up to R16,000 per month for each month of non-compliance, capped at 35 months. It’s essential to differentiate between lawful tax planning and unlawful tax evasion or avoidance, as the latter can result in harsh penalties.
Using Catax to Manage Your Bybit Taxes in South Africa: A Simplified Process

Connect Your Accounts Effortlessly: Start by linking your Bybit and Catax accounts. This process involves generating API keys, which create a secure connection for transferring your transaction details directly to Catax. So It’s a straightforward way to ensure your crypto activity is recorded precisely.
Import Your Transactions Seamlessly: With a single click, Catax will begin to import all your Bybit transactions, including trades, deposits, and withdrawals. It’s akin to having an efficient assistant who meticulously tracks every transaction. However, it’s still prudent for you to review the data to confirm its accuracy.
Carefully check your data: After importing transactions, ensure accuracy. Quickly fixing errors is essential for a reliable tax report.
Generate Your Tax Report with Ease: Catax simplifies the tax calculation process by generating a comprehensive report that clearly outlines your capital gains, losses, and potential deductions. This report is a crucial document that streamlines your tax filing process.
File Accurately with the Authorities: With your checked report ready, the next step is to file it with the South African tax authorities.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Tax rates depend on whether gains are considered capital or revenue. CGT rates can go up to 18% on gains exceeding R40,000 annual exclusion. Income tax rates apply to revenue gains.
SARS can trace crypto transactions and enforce tax obligations through various means, including requiring third-party service providers to submit financial data. SARS has aligned with the Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF) to enhance transparency and combat tax evasion.
Some strategies are to collect losses, receive crypto as gifts, invest through tax-efficient vehicles, hire specialized CPAs, donate crypto, take out loans, move, keep thorough records, and use tax software.
Connect your Bybit and Catax accounts, import transactions seamlessly, review data thoroughly, generate tax reports, and file accurately with the authorities.



